Peripheral Vascular Disease
What is peripheral vascular disease?
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) is a disorder that occurs in the arteries of the circulatory system caused by build up of plaque. Healthy arteries carry oxygen and nutrient-rich blood from the heart to all areas of the body and are smooth and provide no obstruction to blood flow. As we get older these healthy arteries can start to clog up with a sticky substance called plaque made up mostly of fat and cholesterol (sometimes calcium as well) and this process can be accelerated by a number of risk factors such as smoking and diabetes. PVD commonly occurs in the vessels that carry blood to the legs and affects 12-14% of the population.
In peripheral vascular disease the arteries become narrowed or blocked, blood cannot get through to nourish organs and other tissues, causing damage to the tissues and eventually tissue death. The rate at which PVD progresses varies with each individual and depends on many factors, including where in the body the plaque has formed and the person's overall health. If left untreated, peripheral vascular disease can cause pain or aching in the legs, difficulty with walking, resting pain in the foot at night in bed, non-healing sores or infections in the toes or feet and can lead to an amputation in its most severe form. It is also a marker for serious conditions such as heart attack or stroke.
What are the risk factors for peripheral vascular disease?
- Smoking - current smoking or even if you have quit many years ago
- Diabetes - Type 1 or type 2
- Age: Over the age of 50 your risk of PVD begins to rise; it occurs in 20% of those over 75
- History of heart or vascular disease: in your past or in any of your family members
- High blood pressure (hypertension) - even though it may be treated currently with medication
- High cholesterol - even though it may be treated currently with medication
- Obesity
- Lack of exercise
What are the symptoms?
The first noticeable symptom of peripheral vascular disease may be intermittent claudication - this refers to leg discomfort, pain or cramping that develops with activity, is relieved with rest, and recurs upon resuming activity. The pain is often noticed in the calf, but may also be felt in the buttocks or thighs. Intermittent claudication symptoms may also include numbness, weakness, heaviness or fatigue in the leg muscles when walking that are relieved at rest.
The pain can be severe enough to interfere with normal walking. This type of cyclical pain is caused by reduced blood flow to the leg muscles and goes away at rest because the muscles require less blood flow at rest.
Other symptoms of advanced peripheral vascular disease may include:
- A burning or aching pain in the feet and toes while resting, especially at night while lying flat
- Cool skin in the feet
- Redness or other colour changes in the skin
- Increased occurrence of infection
- Toe and foot sores that do not heal
- Leg ulcers or wounds that won't heal or are slow to heal
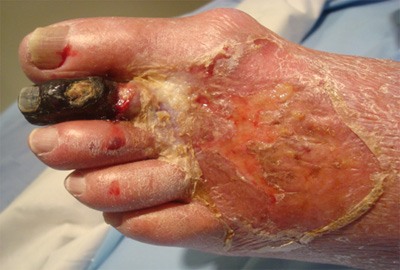
Figure 1
Figure 1 demonstrates the most advanced stage of untreated peripheral vascular disease. The patient was unable to walk; had pain on the left foot from an ulcer; infection in the foot and 2nd toe; gangrene in the 2nd toe
How is PVD diagnosed?
Contact Specialist Vascular Clinic if you are having symptoms of PVD. Early detection of PVD is important so the right treatments can be provided before the disease becomes severe enough to lead to complications, such as heart attack, stroke or amputation.
A thorough history and physical examination is performed in our office. A lack of easily palpable strong pedal pulses in the feet can be a good indication of this condition. The specialist doctor will determine if there is evidence for peripheral vascular disease during your medical history and physical exam. You may then be sent for some investigations to determine the disease severity:
Duplex Ultrasound
A Duplex ultrasound is a simple, non-invasive test used to examine blood circulation. This test may be used to detect a blockage in an artery.
Other tests may include angiography or CT scan.
- During angiography contrast material (dye) is injected into the blood vessels being examined, and X-ray pictures of the inside of the blood vessels are produced to evaluate blood flow and detect possible blockages. This also allows the surgeon to treat the problem at the same time as required.
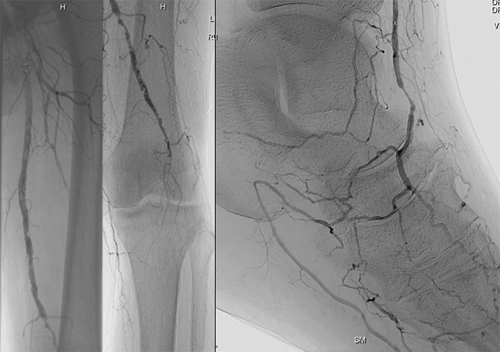
Figure 2
Figure 2 demonstrates an angiogram of the left leg performed on the patient from Figure 1.
- A CT scan is a technique in which multiple X-rays are taken from different angles in a very short period of time. The images are collected by a computer and cross-sectional "slices" of the blood vessel are shown on the monitor.
What is the treatment?
Lifestyle changes, medications, interventional procedures and open bypass surgery are the treatments available for PAD.
Lifestyle changes
Initial treatment of PVD includes making lifestyle changes:
- Quit smoking
- Eat a balanced diet that is high in fiber and low in cholesterol, fat and sodium. Limit fat to 30 percent of your total daily calories.
- Exercise. Begin a regular exercise program, such as walking.
- Manage other related health problems such as high blood pressure, diabetes or high cholesterol.
- Practice good foot and skin care to prevent infection and reduce the risk of complications.
Endovascular surgery
More advanced PVD can be treated with minimally invasive endovascular surgery http://my.clevelandclinic.org/services/atherectomy/vs_atherosclerosis_atherectomy.aspx such as angioplasty (to widen or clear the blocked vessel using a balloon inside the artery), angioplasty with stent placement (to support the cleared vessel and keep it open using a metal stent), or atherectomy (to remove the blockage such as with laser). These procedures are performed under local anaesthesia with sedation without the need for a full general anaesthetic and are performed via a needle in the groin. They do not require surgical incisions or wounds and require < 24 hours in hospital. The benefits in terms of improved blood flow are realised immediately after the procedure. Endovascular surgery is extremely well tolerated even by patients who have been told they are too old or frail for conventional surgery.
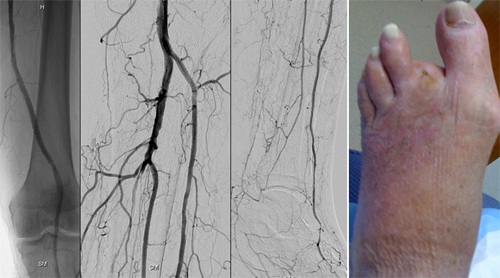
Figure 3
Figure 3 depicts the left leg angiogram of the patient in Figure 2 after endovascular therapy. Note the vast improvement in the circulation to the left leg and foot which resulted in healing. The area of gangrene in the toe was removed only after the circulation was restored.
Open bypass surgery
The vast majority of patients will not require open bypass surgery due to the rapid improvements in minimally invasive endovascular techniques. However, patients who fail to improve with endovascular surgery will be considered for open surgical bypass. This is where a vein or a synthetic plastic tube is used to re-route circulation around the blockage to the lower part of your leg.
If any of these procedures are recommended, Specialist Vascular Clinic will give you more information about the procedures so you will know what to expect.
What are the conditions associated with PVD?
If left untreated, patients with PVD can develop serious health problems, including:
- Heart attack: permanent damage to the heart muscle caused by a lack of blood supply to the heart for an extended time
- Stroke: interruption of the blood flow to the brain leading to weakness, numbness, problems with swallowing, speech, or vision
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA): a temporary interruption in the blood supply to the brain causing symptoms that last less than 24 hours
- Renal artery disease or stenosis: a narrowing or blockage of the artery that supplies blood to the kidney and leads to high blood pressure and worsening kidney function
- Amputation: the removal of part or all of the foot or leg especially in people who also have diabetes
Contact Specialist Vascular Clinic
Contact Specialist Vascular Clinic to make an appointment to be seen by a specialist.
Tel (02) 8999 6309(02) 8999 6309 or request an appointment online.